Aim: Implementing Substitution Cipher
- Polyalphabetic Cipher
Theory: A polyalphabetic cipher is any cipher based on substitution, using multiple substitution alphabets. The Vigenère cipher is probably the best-known example of a polyalphabetic cipher, though it is a simplified special case. The Enigma machine is more complex but still fundamentally a polyalphabetic substitution cipher.
Source Code:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class PolyalphabeticCipher
{
char vignereTable[][]= new char[26][26];
public void GenereatePad() {
char alpharray[] = new char[26];
char c = ‘a’;
for(int x=0;x<26;x++){
alpharray[x] = c;
c++;
}
int i,j,k;
i = 0;
while(i < 26)
{
k = i;
for (j=0;j<26;j++)
{
if (k>=26)
k = 0;
vignereTable[i][j] = alpharray[k++];
}
i++;
}
}
private String key;
public PolyalphabeticCipher(String k)
{
key = k;
}
public String encrypt(String plainText)
{
char[] plainTextArr = plainText.toCharArray();
while(key.length()<plainText.length())
{
key += key;
}
key = key.substring(0,plainText.length());
System.out.println(key);
char [] keyArray = key.toCharArray();
String cipherText = “”;
for(int i=0; i<plainText.length();i++)
{
int rowpos = keyArray[i]-‘a’;
int colpos = plainTextArr[i]-‘a’;
cipherText += vignereTable[rowpos][colpos];
}
return cipherText;
}
public String decrypt(String cipherText)
{
String plainText = “”;
char[] cipherTextArr = cipherText.toCharArray();
char [] keyArray = key.toCharArray();
char [] plainTextArr = new char[keyArray.length];
for(int i=0; i<keyArray.length; i++)
{
int rowpos = keyArray[i] – ‘a’;
int cipherpos = new String(vignereTable[rowpos]).indexOf(cipherTextArr[i]);
plainTextArr[i] = vignereTable[0][cipherpos];
}
plainText = new String(plainTextArr);
return plainText;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter a text key in lower case”);
String keyText = console.nextLine();
PolyalphabeticCipher algo = new PolyalphabeticCipher(keyText);
algo.GenereatePad();
System.out.println(“Enter the plain text”);
String plainText = console.nextLine();
String cipherText = algo.encrypt(plainText);
System.out.println(“The encrypted text is “+cipherText);
plainText = algo.decrypt(cipherText);
System.out.println(“The decrypted text is “+plainText);
}
}
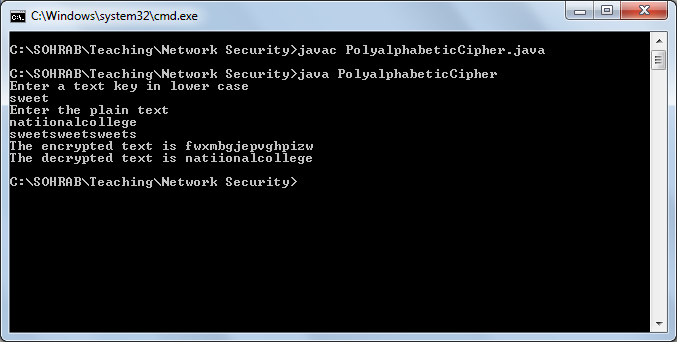
Output:
New innovative Ideas are always welcome. feel free to post below: